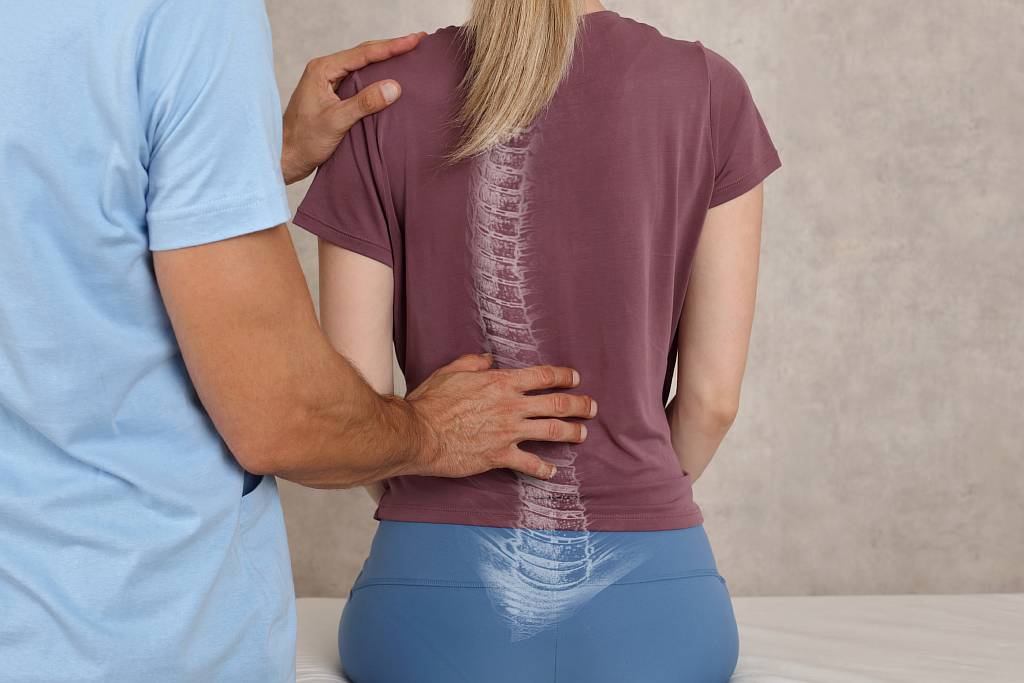
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back
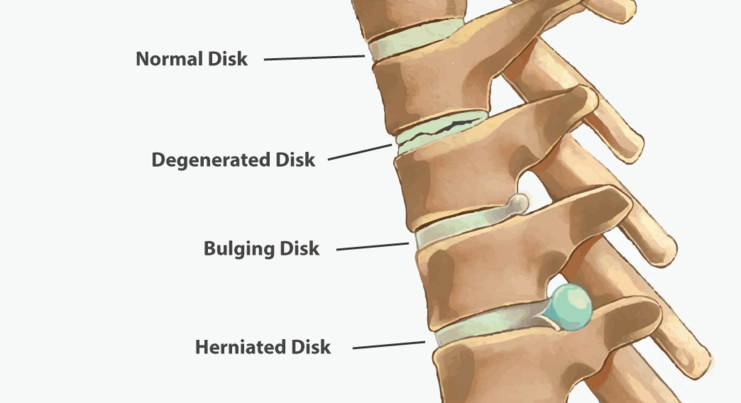
The human spine consists of vertebrae with intervertebral discs between them. Discs allow the spine to move and reduce the stress that is provided by cushioning. A disc consists of the tough external annulus fibrosus and soft inner nucleus pulposus.
If some preconditions are presented, the structure of annulus fibrosus changes, that is called disc degeneration. Thus, spinal disc protrusion occurs, when the intervertebral disc occasionally bulges without the injury of the annulus fibrosus. Finally, spinal disc herniation appears, when an injury of annulus fibrosus facilitates that the small portion of nucleus pulposus bulges out.
Manifestations of the disc herniation depend on its localization. When compression of thecal sac occurs, lumbar pain is the main symptom. If pinched nerve root takes place, a person can complain about radiating pain in groin, buttock, or leg as well as a change in bladder or bowel habits. Not every disc herniation must be treated: often it does not compress the thecal sac and nerve root with an absence of complaints.
Despite spinal discs have a strong structure, they also have some weak spots. There are no blood vessels in the spinal disc. It’s nutrition realized via diffusion (filtering) from the surrounding tissues. However, nutrients are more actively received by disc at the moment of spinal movements.
Modern human lifestyle does not provide necessary physical activity (e.g., office work) that lead to malnutrition of spinal discs and, consequently, decrease of their strength and increase in the risk of injury. Not less destructive effect on the spinal disc is produced by hard physical work, especially if it is related to the lifting of heavy objects and awkward posture (e.g., bending forward while working in the field).
Injury of annulus fibrosus with further forming of a spinal disc herniation can occur even when the trauma of disc happens due to single physical loading (e.g., during lifting the heavy object, especially in front of the body).
Last years more attention is dedicated to genetic predisposition to intervertebral disc degeneration. In particular, numerous studies of twins with different lifestyle demonstrated that 60-70 % of degenerative changes depend on genetic factors. Especially it is typical in cases of disc herniation in adolescents and young adults.
Other risk factors of intervertebral disc herniation include:
- • Smoking. Smoking increases the risk of disc herniation due to the lack of oxygen in the blood. This deprivation leads to malnutrition in body tissues..
- • Weight. Overweight causes additional load in the low back. Sometimes it is impossible to handle the pain without losing weight to the healthy range.
- • Height. Tall people have a greater risk of disc herniation. Tall men are those with height more than 180 cm; tall women are taller than 170 cm.
When leg pain or low back pain occurs, you may need a few days of bed rest. However, you shouldn't stay in bed for more than two-three days due to the risk of the weakness of spinal muscles and increase of pain. During the first weeks, it's not recommended to do any special exercises, fitness, aerobics, jogging, shaping, etc. For maintaining the good physical shape in this period you may swim or walk at a moderate pace. If you feel that pain intensifies, stop immediately any physical activity.
Among medicaments, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Meloxicam, Celebrex, Naproxen, Acetaminophen can temporarily improve a condition. However, do not exceed the suggested daily dosage and overall duration of receiving (10-15 days). Besides, individuals with gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, ulcer) have to be especially careful during taking these medications.
For the diagnostics of spinal disorders, the following methods are decisive:
• Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The magnetic field is used for creating the image of your body. This method is used for confirming localization of the disc herniation and determining affected nerves and structures. MRI is a gold standard for diagnostics of spinal disc herniation.
• Computer tomography (CT). This method demonstrates the state of bones better than MRI, but soft tissues are visualized worse. Ionizing radiation is used in this method.
It’s worth to note that sometimes intervertebral disc herniation can become a dangerous issue. In this situation, late treatment cannot often help to avoid irreversible damage of nervous structures and, consequently, weakness of legs, pelvic floor dysfunction, and paralysis.
Symptoms of serious damage to nerve roots include:
- • Leg pain, especially with dissemination lower than a knee, is a most specific symptom of spinal disc herniation. It is often accompanied by crawling and numbness in the leg.
- • Low back pain often occurs several weeks or months before the leg pain. Pain intensifies while sitting, coughing, sneezing, attempts of bending forward, and changing sides during sleeping.
If you have one of the following symptoms, don’t hesitate to visit a neurosurgeon immediately:
- • You lose control of urination
- • You lose control of defecation
- • ви You feel numbness in the perineum
- • You notice weakness during movements of legs (in foot or knee)
- • You become paralyzed
It's important to remember that the aforementioned signs are the cause of seeking medical help within the first 24 hours. Further delay may lead to irreversible loss of functions (control of pelvic organs, ability to walk).
One of the multimodal and effective treatment methods of spinal disc protrusion and herniation is an Intensive Neurophysiological Rehabilitation System.
To assess the needs of receiving the treatment course by our System, you need:
- To make an appointment for the medical consultation of the doctor from our clinic (MRI and CT results are required)
- To send us the data of your neurological status and imaging (MRI, CT).
